How Does The Speaker Works – The Science Behind Sound!
Speakers convert electrical signals into sound by using components like the voice coil, magnet, and diaphragm. Through electromagnetic interactions, these parts create vibrations, producing sound waves that we hear as audio.
Speakers are essential to our listening experiences, transforming electrical signals into audible sounds that enrich music, movies, and daily life. In this article, we’ll explain the fundamental process of how speakers work, from the components inside to the mechanics that produce sound.
By understanding the basics of speaker technology, you’ll gain a greater appreciation for these complex devices and how they create the sounds you love.
Understanding the Basic Principle of Sound:
To understand how a speaker works, it’s essential first to understand sound. Sound is created by vibrations in the air, which our ears detect as variations in air pressure. When objects vibrate, they cause air molecules around them to compress and decompress, creating a wave of sound that travels through the air. Speakers mimic this natural process by using electrical energy to produce these sound waves.
Key Components Inside a Speaker:

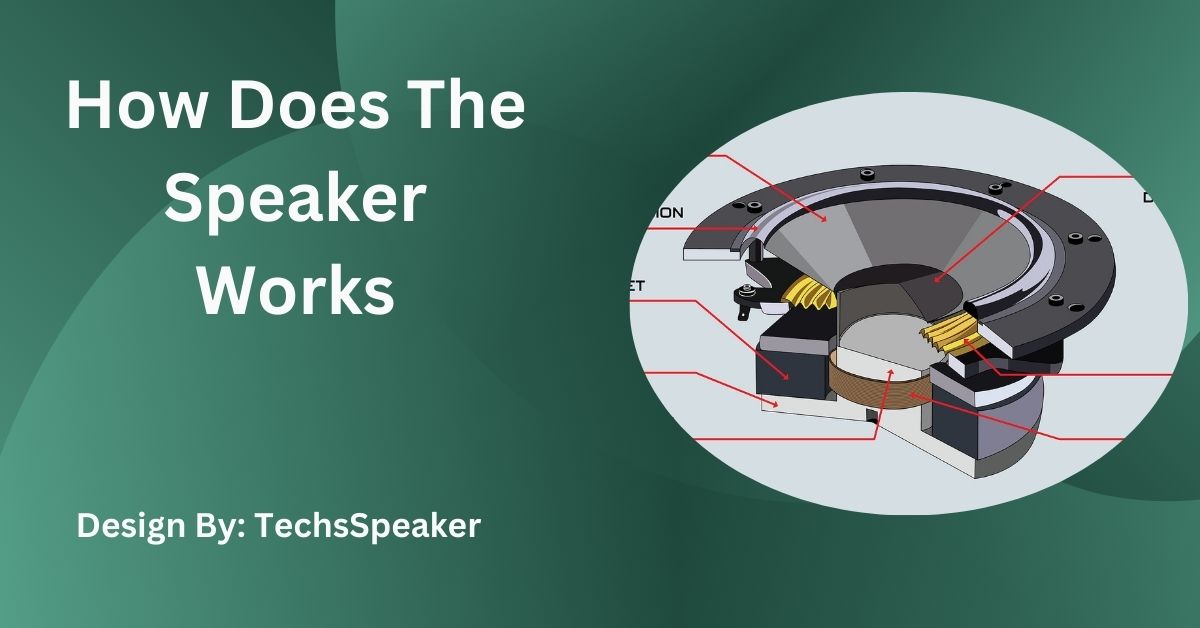
Several vital components work together inside a speaker to transform electrical signals into sound. Let’s break down each of these parts and understand their roles:
Voice Coil
The voice coil is a thin wire wound into a coil and attached to the speaker’s diaphragm, also called the cone. It sits within the magnetic field of the speaker’s magnet and vibrates to create sound. When an electrical signal passes through the voice coil, it becomes an electromagnet, interacting with the permanent magnet to create movement.
Permanent Magnet
The permanent magnet in a speaker provides a stable magnetic field that interacts with the electromagnetism generated by the voice coil. The interaction between the magnetic field and the electric current passing through the voice coil causes the coil to move back and forth, moving the diaphragm and creating sound.
Diaphragm (Cone)
The diaphragm, typically cone-shaped, is the part of the speaker that moves to push air, producing sound waves. When the voice coil moves, it pushes and pulls the diaphragm. The movement of the diaphragm vibrates the air in front of it, creating sound waves that our ears interpret as sound.
Suspension System (Surround and Spider)
The suspension system, made up of the surround and spider, holds the diaphragm and voice coil in place while allowing them to move freely. The surround is the flexible ring around the edge of the diaphragm, and the spider is a flexible piece beneath the diaphragm. Together, they maintain stability and enable controlled movement of the diaphragm.
Speaker Cabinet
The speaker cabinet, or enclosure, is the outer casing that houses and protects the speaker’s components. The design and material of the cabinet can affect sound quality, preventing unwanted vibrations and enhancing acoustics by directing sound waves toward the listener.
How a Speaker Converts Electrical Signals into Sound?
The core process of how a speaker works is based on electromagnetism and vibration. Here’s a simplified step-by-step breakdown of how speakers create sound from electrical signals:
- Receiving the Signal An audio signal, such as from a music player or amplifier, is sent to the speaker as an electrical current.
- Creating Electromagnetism in the Voice Coil The electrical signal flows through the voice coil, creating a magnetic field around it. This temporarily turns the voice coil into an electromagnet, which changes its polarity based on the signal’s frequency.
- Interacting with the Permanent Magnet The electromagnetism generated in the voice coil interacts with the magnetic field of the permanent magnet. When the voice coil’s polarity matches the permanent magnet, it is repelled, and when opposite, it’s attracted. This movement drives the voice coil back and forth.
- Moving the Diaphragm As the voice coil moves, it pushes and pulls the attached diaphragm (or cone). The rapid movement of the diaphragm moves the air around it, creating sound waves.
- Producing Sound Waves These sound waves travel through the air until they reach your ears, where they are processed as sound. The changes in air pressure created by the vibrating diaphragm determine the pitch, volume, and tone of the sound you hear.
Different Types of Speakers and Their Working Mechanisms:
Not all speakers are the same. Different types of speakers are optimized for various purposes, and some use unique mechanisms to produce sound. Here’s a quick overview of different types of speakers:
1. Dynamic Speakers
Dynamic speakers, also known as moving-coil speakers, are the most common. They work using the electromagnetic process described above, with a voice coil, magnet, and diaphragm.
2. Electrostatic Speakers
Electrostatic speakers use a thin, charged diaphragm between two conductive panels, or stators. When an audio signal is applied, it creates an electrostatic field that moves the diaphragm, creating sound without a magnet or voice coil.
3. Planar Magnetic Speakers
Planar magnetic speakers use a thin diaphragm embedded with a conductive pattern. Magnets are placed on either side of the diaphragm. When an electric current flows through the conductive pattern, it interacts with the magnets, moving the diaphragm to create sound.
4. Horn Speakers
Horn speakers use a horn structure to amplify sound. Sound waves generated by a diaphragm travel through a flared horn shape, which naturally amplifies the sound without additional power.
Also Read: Are Speaker Wires Dangerous – A Depth Analysis!
Factors That Affect Speaker Sound Quality:
Speaker sound quality can vary based on several factors. Here are key elements that influence the performance and clarity of a speaker:
- Speaker Design and Materials: The design and material of each component, especially the diaphragm, play a critical role in sound clarity and range.
- Speaker Size: Larger speakers generally produce deeper bass, while smaller speakers may focus more on higher frequencies.
- Cabinet Design: The type of enclosure affects acoustics and reduces unwanted vibrations that might distort sound quality.
- Power Handling: A speaker’s power handling capacity determines the maximum volume and clarity it can achieve without distortion.
- Frequency Response: A speaker’s ability to reproduce low, mid, and high frequencies impacts its sound quality, providing a fuller audio experience.
Understanding Frequency and Volume in Speaker Output:
Two primary characteristics of sound that a speaker produces are frequency and volume:
Frequency:
Measured in Hertz (Hz), frequency represents the pitch of the sound. Higher frequencies create higher-pitched sounds, while lower frequencies create deeper bass sounds. Full-range speakers aim to reproduce a wide range of frequencies accurately.
Volume:
Volume is measured in decibels (dB) and is determined by the amplitude of the sound wave. The larger the amplitude, the louder the sound. The volume a speaker can produce depends on the power of the audio signal and the speaker’s power-handling capacity.
Tips for Maximizing Speaker Performance:

Properly setting up and caring for speakers can significantly improve sound quality. Here are tips for getting the best out of your speakers:
- Choose the Right Position: Placing speakers at ear level and angling them toward the listening area creates a more immersive experience.
- Use High-Quality Audio Sources: High-quality audio files or devices help avoid signal loss and maintain sound clarity.
- Reduce Interference: Keep speaker wires and power cords separate to avoid electromagnetic interference, especially in complex audio setups.
- Regular Maintenance: Dusting and occasionally cleaning speakers can prevent dust buildup, which may affect sound clarity over time.
Advantages of Understanding How Speakers Work:
Understanding how speakers work provides several benefits:
- Better Purchasing Decisions: Knowing the basic components and types of speakers helps you choose the right model for your needs.
- Optimal Setup: You can position and connect speakers more effectively, improving sound quality and durability.
- Enhanced Safety: Familiarity with speaker technology helps prevent issues like overheating or damage to the components.
FAQs:
1. What is the role of the voice coil in a speaker?
The voice coil interacts with the speaker’s magnet to produce movement, causing the diaphragm to vibrate and push air, creating sound waves that reach our ears as audio.
2. How does a speaker produce different sound frequencies?
The frequency of sound depends on the speed of diaphragm vibrations. Faster vibrations create high frequencies, while slower ones produce lower frequencies, resulting in varying sound pitches.
3. What is the purpose of the speaker cabinet?
The speaker cabinet encloses and protects internal parts, controls vibrations, and directs sound toward listeners, enhancing sound quality by reducing unwanted noise and improving acoustics.
4. How do electrostatic speakers differ from dynamic speakers?
Electrostatic speakers use an electrostatic field to move a thin diaphragm, unlike dynamic speakers, which use a voice coil and magnet. This design provides a more detailed, natural sound.
5. What affects the sound quality of a speaker?
Speaker sound quality is influenced by factors like component materials, cabinet design, speaker size, power handling, and frequency response, all contributing to clarity, volume, and overall audio experience.
Conclusion:
Understanding how speakers work highlights the sophistication behind transforming electrical signals into sound. Through components like the voice coil, diaphragm, and magnet, speakers create vibrations that generate sound waves, bringing audio to life. Knowing these fundamentals helps you make informed choices, optimize speaker setup, and appreciate the technology within. This knowledge not only enhances your listening experience but also supports the longevity and performance of your audio equipment.