Amplifier classes differ in efficiency, sound quality, and application. Class A, B, AB, D, and H offer various benefits for home, professional, and portable audio setups.
Whether you’re setting up a state-of-the-art home theater system or designing professional audio equipment, understanding the different classes of speaker amplifiers is key to getting the best performance.
Amplifiers are responsible for boosting electrical signals and driving your speakers, but not all amplifiers are built the same. They are categorized into different classes, each with its own characteristics, strengths, and weaknesses.
Let’s break down the most common classes of amplifiers and help you understand which one might be right for your needs.
Amplifier “classes” refer to how the amplifier’s electrical components function to amplify the audio signal. The biggest differentiators between classes are:
- Efficiency (how much power is converted into audio output vs. dissipated as heat)
- Sound quality (distortion levels and audio fidelity)
- Use case (professional sound systems, home audio, portable speakers, etc.)
Now, let’s explore the most common amplifier classes.
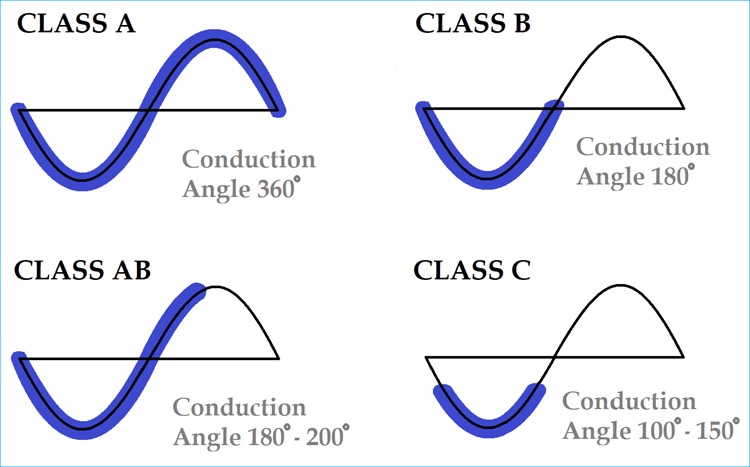
Class A amplifiers are known for their exceptional sound quality. They use a single transistor or vacuum tube that is always conducting, which means the signal is amplified linearly without any interruptions.
- Sound Quality: Produces high-fidelity, low-distortion sound.
- Efficiency: Very low (typically around 20-30%) due to constant power consumption, even when idle.
- Heat Output: Runs hot as a significant amount of energy is wasted as heat.
- Audiophiles and high-end home audio systems where sound quality is paramount.
Class B amplifiers use two transistors, each responsible for amplifying one half of the audio signal (positive and negative). This design improves efficiency.
- Efficiency: Higher than Class A (around 50%) because power is only consumed when amplifying signals.
- Sound Quality: May produce some distortion at the signal crossover point (called “crossover distortion”).
- Applications that prioritize efficiency over pristine sound quality, such as older audio systems.
Class AB combines the best of both Class A and Class B designs. The transistors conduct slightly in Class A mode during low-level signals and switch to Class B during high-level signals.
- Sound Quality: Great balance of sound quality with reduced distortion compared to Class B.
- Efficiency: Improved efficiency over Class A (40-60%).
- Versatility: Commonly used across many audio applications.
- Home theater systems, professional sound setups, and car audio.
Class D amplifiers, often called “digital amplifiers,” use a completely different approach. They rapidly switch the transistors on and off to generate a pulse-width-modulated signal, which is then filtered into an audio signal.
- Efficiency: Extremely high (up to 90%) because the transistors are either fully on or off, minimizing heat loss.
- Sound Quality: Generally excellent, though some purists argue it’s not as “warm” as Class A or AB.
- Compact Design: Smaller and lighter due to reduced heat dissipation.
- Portable speakers, subwoofers, and modern home audio systems where power efficiency is critical.
Class H amplifiers are an advanced version of Class AB. They adjust the voltage rails in real-time based on the input signal, ensuring just enough power is delivered.
- Efficiency: Higher than Class AB by reducing excess power use.
- Sound Quality: Maintains clarity similar to Class AB with less power consumption.
- Heat Output: Lower compared to Class AB.
- Professional audio setups, especially in live performances where efficiency and sound quality both matter.
| Class | Sound Quality | Efficiency | Heat Output | Best For |
| Class A | Exceptional | Low (20-30%) | High | Audiophiles, premium home audio setups |
| Class B | Moderate | Moderate (50%) | Moderate | Older audio systems |
| Class AB | Great | Moderate (40-60%) | Moderate | Home theater, professional sound |
| Class D | Excellent | High (up to 90%) | Low | Portable speakers, subwoofers, modern audio |
| Class H | Great | Higher than AB | Lower | Live performances, professional audio |
The right amplifier class depends on your needs:
- If sound quality is your top priority: Go for Class A or Class AB.
- If you need efficiency and portability: Class D is the best choice.
- If you want a balance between sound and efficiency: Opt for Class AB or Class H.
Choosing the right amplifier is about understanding your priorities. Are you building a high-fidelity stereo setup for your living room? Or do you need a powerful, efficient amplifier for a portable speaker? Each class serves a purpose.
Also Read: What Is A Three Way Speaker – Everything You Need to Know!
When selecting an amplifier class, it’s important to consider the following factors:
- Understanding the power efficiency of different amplifier classes can help you determine the most suitable option for your needs.
- Evaluate the power consumption and heat dissipation levels of each class to ensure optimal performance and minimize energy waste.
- The amplifier class you choose will have a significant impact on the sound quality of your audio system.
- Assess the level of audio fidelity and accuracy offered by each class to ensure it aligns with your expectations and requirements.
- Consider the specific application and usage scenario for your amplifier.
- Different amplifier classes are better suited for specific purposes, such as home audio setups, professional sound systems, portable speakers, or live performances.
- Determine your budget and assess the cost-effectiveness of each amplifier class.
- Factor in not only the initial investment but also long-term maintenance costs and potential future upgrades.
By considering these factors, you can make an informed decision when choosing the amplifier class that best suits your needs, ensuring an optimal audio experience for your specific requirements.
Amplifier classes differ in efficiency, sound quality, and use case. Class A prioritizes sound quality, Class D focuses on efficiency, and Class AB offers a balance.
Class A amplifiers are best for high-fidelity audio due to their exceptional sound quality and low distortion, making them ideal for audiophiles and premium home audio systems.
Class D amplifiers are popular in portable speakers due to their high efficiency (up to 90%), compact design, and low heat output, making them suitable for modern, energy-efficient audio devices.
Yes, Class H amplifiers are ideal for live performances due to their high efficiency, reduced heat output, and ability to maintain sound clarity with lower power consumption.
Consider power efficiency, sound quality, application, and budget when choosing an amplifier class. These factors will help you select the best amplifier for your specific audio needs.
Understanding the different classes of speaker amplifiers is crucial for optimizing your audio system. Class A and AB amplifiers excel in sound quality, while Class D and H offer high efficiency and are suitable for portable and professional setups. When choosing an amplifier class, consider factors such as power efficiency, sound quality, application, and budget to ensure the best performance for your specific needs. By making an informed choice, you can achieve the perfect balance between audio fidelity and efficiency.
